Table of Contents
What are commodities?
Why trade commodities?
Types of commodities
What drives commodity prices?
Trading commodities with CFDs
How to place a commodity trade on TBanque
Alternative ways of trading commodities on TBanque
Risks of trading commodities
Summary
Glossary
What are commodities?
A commodity is a basic good or raw material that is used to produce more complex goods. You can think of commodities as the building blocks of the global economy theyre used to create products that we rely on every day. Examples of commodities include oil, gold, copper, and sugar.
What separates commodities from other goods is the fact that they are standardised and interchangeable. This means that two equivalent units of the same commodity will be more or less identical, no matter where they are produced. For example, one ounce of gold from a mine in Brazil will be identical to one ounce of gold from a mine in Australia.
Commodity trading
Commodities have been traded for thousands of years. In the past, they were traded physically. Today, however, commodity trading takes place on exchanges around the world such as the London Metal Exchange (LME) and the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME). To trade commodities, you need an account with a trading platform that offers access to the commodity markets.
At eToro, trading commodities is straightforward. eToros platform is easy to use and enables traders and investors to trade a wide range of commodities.
Why trade commodities?
There are a number of advantages to trading commodities. Here are some of the main advantages:
Plenty of trading opportunities: commodity prices tend to be quite volatile which is an advantage for traders as it means that there are always plenty of trading opportunities. Traders can trade in both directions too, meaning its possible to capitalise on both upward price movements and downward price movements.
- Leverage can boost gains: when trading commodities its possible to use leverage to control a large amount of money with just a small deposit. This is an advantage because it can potentially magnify your gains. On the downside, however, leverage can also increase your losses, so its important to be aware of the risks. TBanque offers leverage of up to x10 (meaning you can trade $1,000 with a deposit of $100) on most commodities and up to x20 on gold.
- Around the clock trading: commodity markets are open for a large part of the week. This means that you can trade on your own schedule.
- Portfolio diversification: commodities tend to have low correlations to traditional asset classes such as stocks and bonds. For example, gold, which is seen as a safe-haven asset, often rises during periods of economic uncertainty when stocks are falling. This means that commodities can add diversification to a portfolio and potentially help traders and investors lower their overall portfolio risk.
- A hedge against inflation: In the long run, traditional currencies tend to lose their purchasing power due to inflation (the increases in the prices of goods and services over time). Commodities can protect investors against inflation because commodity prices often rise during periods of high inflation.
Types of commodities
Commodities can generally be divided into three main categories: metals, energy, and agricultural. Heres a look at each of these categories.
Metals
Metal commodities are commonly used in manufacturing and construction. Some metals, such as gold and silver, are also used in jewellery and for investment purposes.
Examples of metal commodities include:
Energy
Energy commodities play a crucial role in keeping the global economy ticking over. Without energy, we would be unable to transport people and goods across the world, power factories, or heat our homes.
Examples of energy commodities include:
Agricultural
Agricultural commodities are crops and animals that are grown or raised on farmland. Most agricultural commodities are used to produce food, however, some have industrial uses.
Examples of agricultural commodities include:
Hard vs soft commodities
Commodities are also often classified as either hard or soft commodities.
Hard commodities are generally natural resources that are mined or extracted out of the ground. Examples include gold, copper, and oil.
Soft commodities are typically agricultural products or livestock that are grown or raised on a farm. Examples include sugar, cotton, and wheat.
What drives commodity prices?
Every commodity has unique factors that affect its price.
However, overall, the major driver of commodity prices is supply and demand. Higher demand for a commodity pushes its prices up, while excess supply of a commodity pushes its price down.
Supply and demand can be impacted by many different factors. Heres a look at some of the main factors.
Demand
Key drivers of commodity demand include:
- The health of the global economy: during periods of strong economic growth, demand for many commodities tends to be high due to the fact there is more construction and manufacturing activity. Conversely, during periods of weak economic growth, commodity demand tends to be lower due to the fact there is less construction and manufacturing activity.
- Growth in the emerging markets: fast-growing emerging market countries such as China and India are a major source of commodity demand. These countries need commodities to build infrastructure, fuel their factories, and feed their growing populations. During periods of economic expansion in the emerging markets, demand for commodities tends to be high.
- Consumer trends: consumer trends also play a key role in commodity demand. For example, consumer demand for jewellery can boost demand for gold. Similarly, demand for cars can have an impact on the demand for platinum, as this is used to make catalytic converters, which help to reduce vehicle emissions.
- Manufacturing trends: demand can be impacted negatively by commodity substitution. If a particular commodity becomes too expensive, buyers will look for cheaper alternatives. A good example here is copper, which is used in a wide range of industrial applications. As the price of copper has risen, many manufacturers have used aluminum as a substitute.
- The strength of the US dollar: most commodities are priced in US dollars. When the US dollar falls, it means commodities are less expensive in other currencies which can lead to an increase in demand. Historically, the prices of commodities have tended to rise when the value of the US dollar has weakened against other major currencies. This inverse relationship does not hold all of the time, however.
Commodity demand example
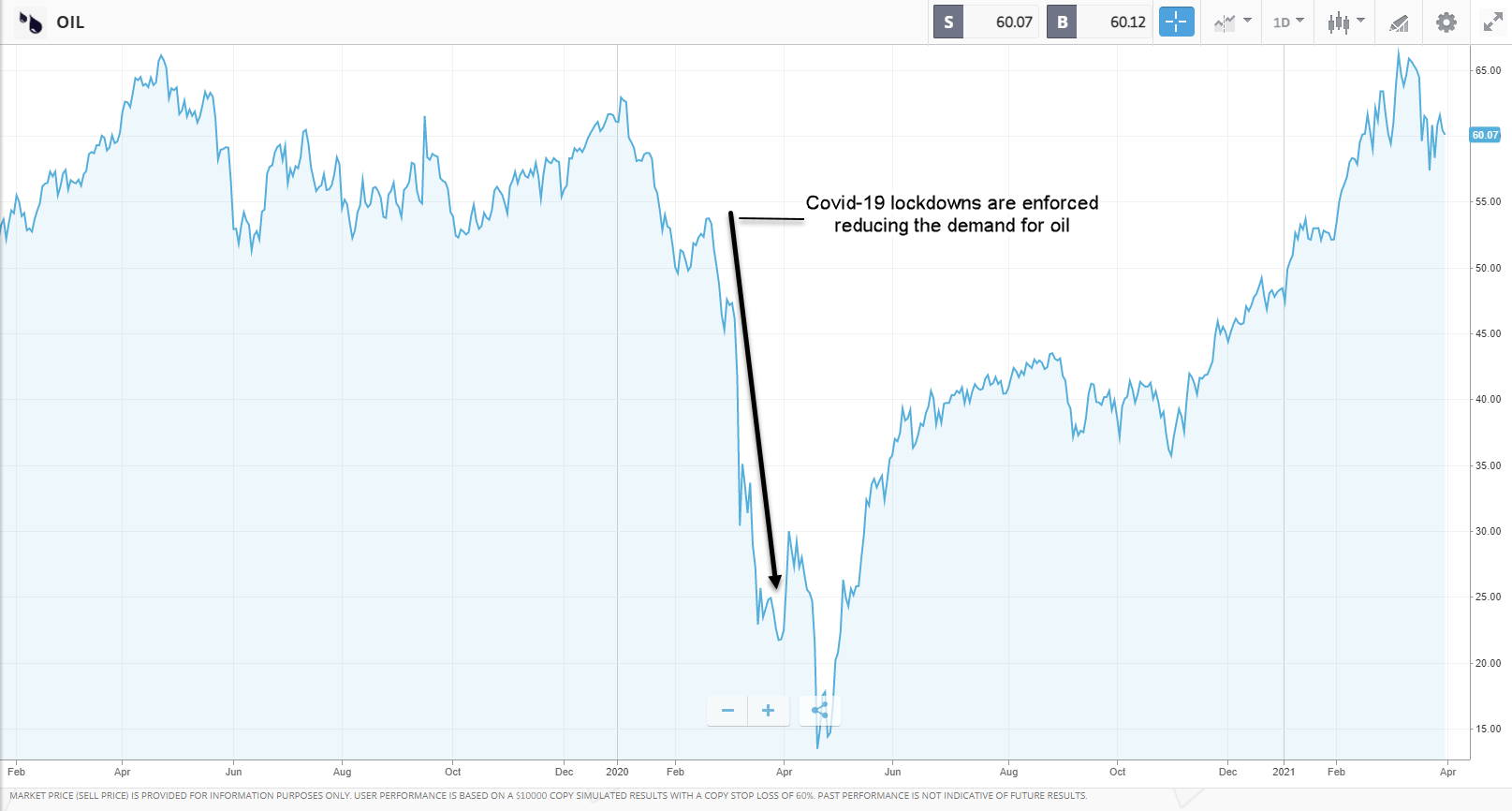
When the Covid-19 pandemic sent the world into lockdown mode in early 2020, the global travel industry ground to a halt. As a result, demand for oil a key ingredient in gasoline and aviation fuel plummeted. This resulted in a spectacular collapse in the price of oil.
Supply
Key drivers of commodity supply include:
- Government intervention: governments can play a key role in commodity supply by introducing production constraints. For example, the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), an intergovernmental oil organisation, has been known to enforce supply cuts in the oil market in order to bolster oil prices.
- Geopolitical events: conflicts between countries, terrorist attacks, trade wars, social unrest, and closures of important transport routes can all impact commodity supply.
- Weather: the weather can also play a major role in the supply of agricultural commodities such as sugar, cotton, and cocoa. These kinds of commodities require consistent weather cycles for farmers to grow crops.
Commodity supply example
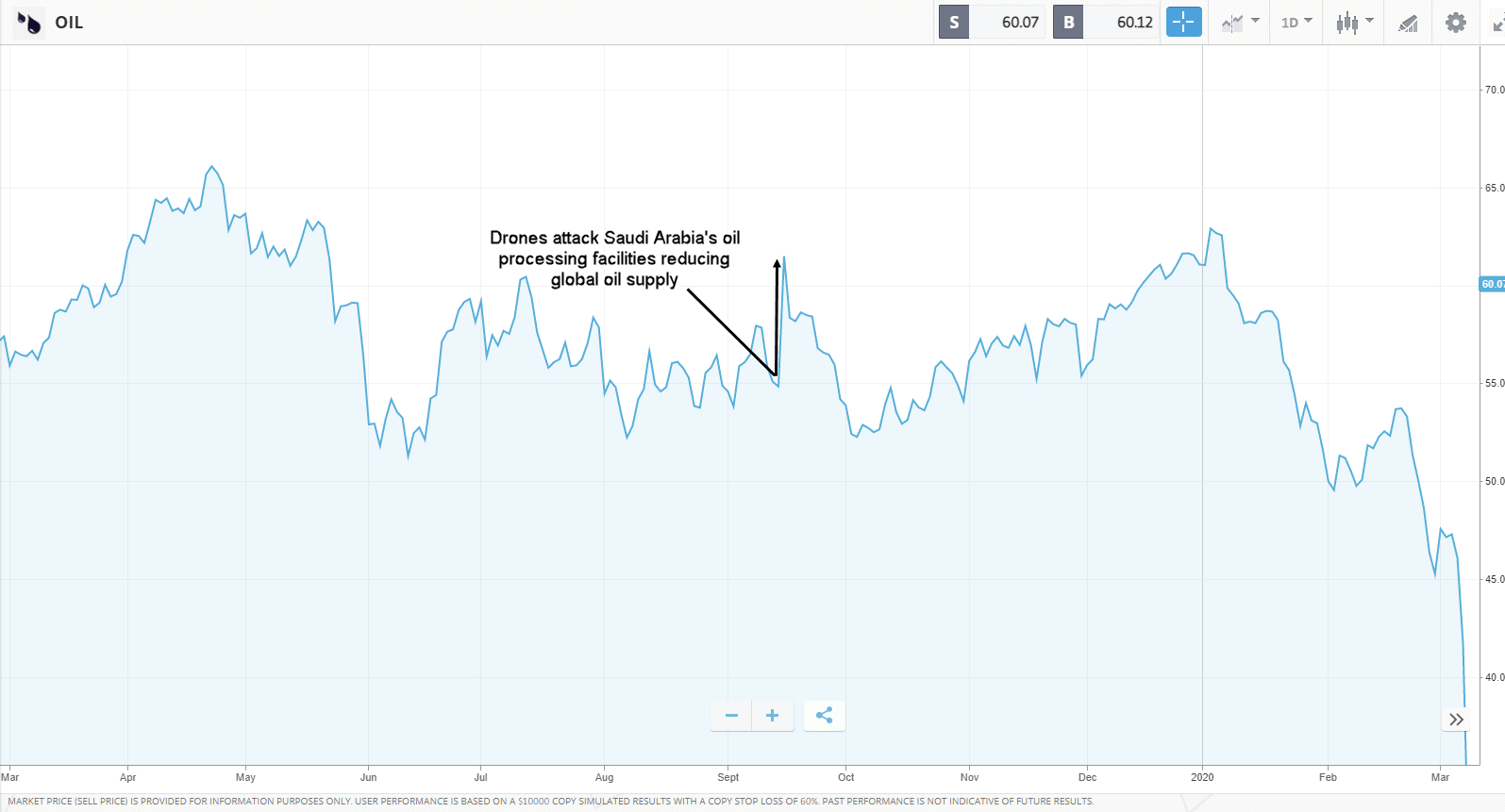
On 14 September 2019, a swarm of explosive drones attacked Saudi Arabias Saudi Aramco oil processing facilities. The drone attack caused large fires at the facilities which ultimately cut Saudi Arabias oil production by about half representing about 5% of global oil production temporarily. This sudden decrease in oil supply caused oil prices to surge higher.
Trading commodities with CFDs
There are a number of ways to trade commodities.
One of the easiest ways, however, is through Contracts For Difference (CFDs).
CFDs are financial instruments that offer traders and investors the opportunity to profit from the price movements of a security without actually owning the underlying security.
Trading commodities through CFDs has a number of advantages:
- CFDs enable you to profit from price movements of a commodity without having to take delivery or arrange supply of the commodity itself (i.e. a barrel of oil or a bar of gold bullion).
- CFDs enable you to use leverage to increase your exposure to a commodity.
- There are typically no transaction fees associated with CFD trades. The main form of fee that traders pay is the spread between the buy price and the sell price of the trade*.
Heres how trading commodities with CFDs works:
- You choose the commodity you wish to trade. For example, oil.
- You set up the CFD trade by selecting:
- Buy or sell. Youd select buy if you believe the commoditys price is going to rise. This is called going long. Youd select sell if you believe the commoditys price is going to fall. This is called going short.
- The amount of money or number of units you wish to trade.
- The leverage involved.
- Your stop loss or take profit orders.
- You open the position.
- The position remains open until you either close it or it is closed by a stop loss or take profit order, or the expiration of the contract.
* CFD positions that stay open overnight incur a small fee, relative to the value of the position. This is essentially an interest payment to cover the cost of the leverage that you use overnight.
How to place a commodity trade on TBanque
Placing a commodity trade on TBanque using CFDs is straightforward.
Heres how to do it:
- Login or create an account by going to www.etoro.com
- Head to Trade Markets, and then select Commodities to access the full list of commodities
- Select the commodity that you wish to buy or sell, then select Trade
- Select BUY or SELL depending on the direction you wish to trade
- Enter the amount or number of units you wish to trade
- Set the stop loss, leverage, and take profit parametres
- Select Open Trade
Thats it. It really is very simple.
Alternative ways of trading commodities on TBanque
Its worth pointing out that there are other ways to trade commodities on TBanque.
One alternative to trading CFDs is trading exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
ETFs are investment funds that are designed to track the performance of a particular asset. They are traded on the stock market.
On TBanque, there are a number of ETFs that track the prices of commodities.
Examples include:
- The SPDR Gold ETF (ticker: GLD), which tracks the price of gold.
- The iShares Silver Trust ETF (ticker: SLV), which tracks the price of silver.
- The Teucrium Corn Fund ETF (ticker: CORN), which tracks the price of corn.
- The Teucrium Wheat Fund ETF (ticker: WEAT), which tracks the price of wheat.
Youll find more information on ETFs in our Beginners Guide to ETFs.
Its also possible to profit from commodity price movements by trading the stocks of companies that are involved in commodity production.
Examples of these kinds of stocks include:
- BP (ticker: BP.L), which is one of the largest oil producers in the world.
- Barrick Gold (ticker: GOLD), which is one of the largest gold mining companies in the world.
- Southern Copper Corp (ticker: SCCO), which is one of the largest copper producers in the world.
On TBanque, you can invest in stocks commission free.
Youll find more information on stocks in our Beginners Guide to Stocks.
Risks of trading commodities
Any form of investing or trading involves risks and commodity trading is no different.
Two of the main risks to be aware of with commodity trading are:
- Price risk: price risk refers to the risks associated with the fluctuations in commodity prices. Commodity prices can be extremely volatile and while this volatility can create trading opportunities, it can also be a risk factor. Unfavourable price movements can result in significant losses for traders. If you do not have sufficient funds in your account to cover potential losses, your positions may be automatically closed.
- Leverage risk: while leverage is a powerful tool that can magnify trading gains, it can also work against you by magnifying trading losses. If a large amount of leverage is used to trade, even a relatively small price movement in the wrong direction can result in substantial losses. Its important to be aware that losses can exceed the amount invested.
Risk management strategies
You can never eliminate risk completely when trading commodities, however, you can reduce it by focusing on risk management.
Three strategies that can help reduce risk include:
- Determining your optimal position size: before you start trading commodities, you should determine your optimal position size for each trade. A good rule of thumb is to avoid risking more than 2% of your capital on any single trade. Trading more than 2% per trade could expose you to losses that are hard to recover from.
- Putting stop losses in place: stop losses are a fundamental component of a robust risk management strategy. Stop losses help minimise trading losses by closing out losing positions before large losses build up.
- Diversifying your portfolio: a portfolio that tracks a wide range of assets will have a lower level of risk than a portfolio that simply focuses on one asset. By diversifying your portfolio across multiple asset classes such as stocks, ETFs, bonds, and commodities, you can lower your overall portfolio risk.
Summary
- A commodity is a basic good or raw material that is used to produce more complex goods. Examples include oil, gold, copper, and sugar.
- What separates commodities from other goods is the fact that they are standardised and interchangeable. This means that two equivalent units of the same commodity will be more or less identical, no matter where they are produced.
- There are a number of advantages to trading commodities. Not only do commodities offer plenty of trading opportunities but they can also help diversify an investment portfolio.
- The three main types of commodities are metals, energy, and agricultural commodities. Commodities are also often classified as hard or soft commodities.
- Commodity prices are impacted by supply and demand. Demand can be affected by the health of the economy, growth in the emerging markets, consumer trends, manufacturing trends, and the strength of the US dollar. Supply can be affected by government policies, geopolitical events, and the weather.
- There are a number of ways to trade commodities, however, CFDs are one of the easiest ways. CFDs are financial instruments that offer traders and investors the opportunity to profit from the price movements of a security without actually owning the underlying security.
- The risks of trading commodities include price risk and leverage risk. Risk can be reduced by focusing on risk management strategies.
- At eToro, trading commodities is straightforward. eToros platform is easy to use and enables traders and investors to trade a wide range of commodities.
Glossary
- COMMODITY A basic good or raw material that is used to produce more complex goods.
- CFD contract for difference. A financial instrument that enables you to profit from the price movements of securities without actually owning the underlying security
- GOING LONG buying a security
- GOING SHORT selling a security
- LEVERAGE a loan that enables you to control more money than you have staked on a trade
- RISK the amount of capital exposed on any single trade
- RISK MANAGEMENT focusing on risk when trading in order to minimise losses
- SPREAD the difference between the buy and the sell price. This is also the cost of placing the trade
- STOP LOSS an order designed to minimise losses
- TAKE PROFIT an order to close a trade at a certain profit level
Discover commodities trading on TBanque now
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any financial instruments. This material has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and has not been prepared in accordance with the legal and regulatory requirements to promote independent research. Any references to past performance of a financial instrument, index or a packaged investment product are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. TBanque makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content of this guide. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose.